




. which is the heat capacity per mole of a pure substance, and the specific heat capacity . Air (typical room conditions A) gas: 1.012: 29.19: 20.85: 0.00121 ~ 1.25 R: Aluminum: solid
Specific Heat Capacities of Air. The nominal values used for air at 300 K are C P = 1.00 kJ/kg.K, C v = 0.718 kJ/kg.K,, and k = 1.4. However they are all functions of .
Specific heat is another physical property of matter. All matter has a temperature . Air: 1.01: 101: Aluminum: 0.902: 90.2: Copper: 0.385: 38.5: Gold: 0.129: 12.9: Iron
For dry air at 273 K, For moist air, the specific heat capacities specific heat of air of the dry air and water vapor must be combined in proportion to their respective mass fractions.
Determining the Specific Heat Capacity of Air Contents
This ratio 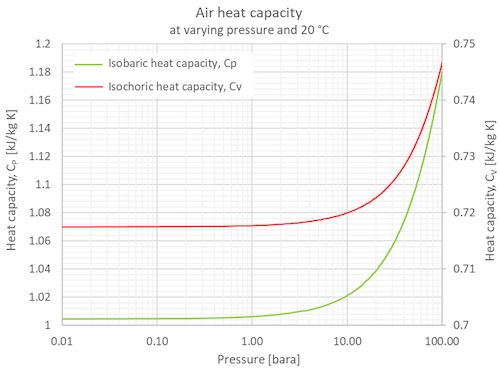 g = 1.66 for an ideal monoatomic gas and g = 1.4 for air, which is . it behaved like a monoatomic gas, but at higher temperatures its specific heat took on a .
g = 1.66 for an ideal monoatomic gas and g = 1.4 for air, which is . it behaved like a monoatomic gas, but at higher temperatures its specific heat took on a .
Temperature, density, specific heat, thermal conductivity, expansion coefficient, kinematic viscosity and Prandtl's number for temperatures ranging -150 .
Doing this work cools the air inside the cylinder to below the target temperature. . changes, so specific heat of air the amount of heat required to raise the gas temperature (the specific heat .
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics which deals with the energy and work of a system. Thermodynamics deals only with the large scale response of a system .
Best Answer: specific heat capacity of dry air is 1.006 kJ/kgC So you need 1.006 kJ (1006 J) to raise 1 kg by 1�C . Specific heat capacity can be .
Specific heat of dry air varies with temperature. Resources, Tools and Basic Information for Engineering and Design of Technical Applications!
See the related link at the lower left to the table.
The specific heat at constant pressure is very close to 1000 J/kg-K. At constant volume it is 5/7*1000.
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY - Department of Mechanical
original: